 Attaining an edge by understanding the flow of capital is an important concept toward your trading success. Gauging investor sentiment and following the smart money will provide you with the confidence you need to generate robust returns. A tool that can guide you and help you determine where the smart money is risking their capital is the Commitment of Traders (COT) report. By evaluating the information on this report you can determine the trend in” smart money” risk positioning as well as investor sentiment.
Attaining an edge by understanding the flow of capital is an important concept toward your trading success. Gauging investor sentiment and following the smart money will provide you with the confidence you need to generate robust returns. A tool that can guide you and help you determine where the smart money is risking their capital is the Commitment of Traders (COT) report. By evaluating the information on this report you can determine the trend in” smart money” risk positioning as well as investor sentiment.
The COT is a report released each week that will provide you with a glimpse of what positions managed money, small speculators, and commercial producers are taking in nearly every futures category. The report is disseminated by the Futures Trading Commission and is issued every Friday during the week. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission CFTC COT report has been published since 1986 and includes several financial vehicles including a report called the currency COT report.
The COT Report
The COT report (also known as the COT index) is broadcast by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission. The CFTC is an independent United States agency which was created in 1974. Originally, the CFTC was focused on agricultural commodities which traded in the United States for over one hundred and fifty years and have also been under federal regulation since the early 1920’s.
During 1970’s the trading of futures contracts expanded quickly beyond agricultural commodities to incorporate a multitude of other financial instruments which included; foreign currencies, United States and foreign government securities and United States/foreign Equity indices.
In late 2000, Congress renewed the CFTC’s mandate and passed what is known today as the Commodity Futures Modernization Act (CFMA). In short the Commodity Futures Modernization Act developed a joint regulatory body between the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the CFTC.
The purpose of the regulatory body is to regulate single stock futures which started trading during November 2002. In 2003, the size of the swaps market increased dramatically compared to their introduction during the late 1970’s. The Dodd Frank Act which was created in 2010 expanded the CFTC’s control into the swaps market to help marshal reckless trading within the swaps market.
What are the responsibilities of the CFTC? The CFTC has several responsibilities. One of the primary responsibilities of the CFTC is to support efficiencies along with competiveness within the futures markets. In addition, the CFTC is a watch dog to ensure integrity as well as help prevent fraud, manipulation and abusive trading practices within the futures markets. Similar to the SEC, the CFTC does not directly regulate the safety of individual organizations. COT data is obtained by the CFTC for markets which have 20 or more traders holding active positions.
The COT report is a strong analytical tool because it offers updated information related to every futures markets. In addition, the COT report is readily available on the most frequently traded futures contracts, which is generally the prompt contract. For instance, the COT report is available on currency contracts which allow COT analysis in currencies. The information released by the CFTC is somewhat cryptic, which makes learning how to read the COT report, a minor challenge.
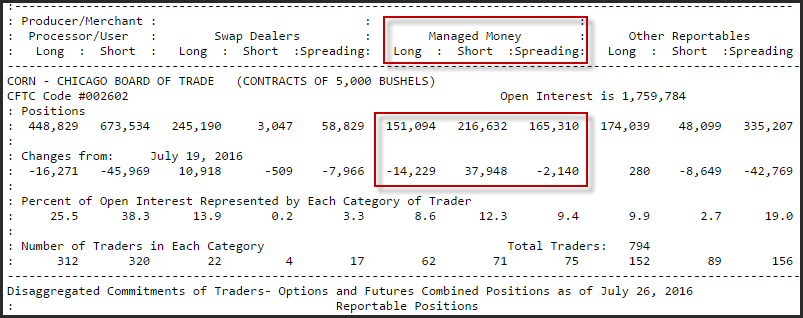
For example, in the week ending July 26, 2016, managed money increased short position in futures and options by nearly 38K contracts while reducing short position in futures and options by slightly more than 14K contracts. The total open interest for managed money is 151,094 long futures and options versus 216, 362 short futures and options.
It is important to understand the different groups of trader who leverage the COT report. There are three types of trading groups who make up the COT report which include; commercial traders or swap dealers, managed money or non-Commercial traders and non-reporting traders.
Again, when reviewing the Commitment of Traders data and currency information (also known as the forex Commitment of Traders Data) it is important to note that the data associated to the COT report is broken down into different trader types as well as the size of their positions.
Typically, the largest positions are held by the commercial institutions or what is also known as hedgers whose intent is taking delivery of the commodity. A good example of a commercial trader would be a soybean farmer who wants to hedge soybean crop prices to ensure that they can sell their inventory of soybean at a defined set price.
The second largest group/player is the large speculators which typically consist of Hedge Funds along with CTA trading Pools. The position’s taken by this group are speculative and these traders usually do not have intent on taking delivery of the underlying commodities which they are trading.
This group is strictly trading for profit and their moves can help you determine the underlying trend in a specific capital market. Hedge fund generally do not intend to take delivery of the commodity and since the non-commercial traders are speculating on price, they are more likely to flinch, when new information is revealed and everyone starts heading toward the exits at the same time.
The last and final group is deemed the small speculators. This group of traders are considered of the small guy or one lot crowd. This groups of traders are also usually seen as the group which are the most ill-informed.
There is a term frequently used amongst commodities traders and that is “following the smart money”. What does following the smart money mean or who is the smart money? When doing your homework and researching the historical COT reports, you will clearly see at specific times where the major players have positioned themselves. Researching the COT report will help the trader enter on the correct side of the market.
How to Evaluate Futures and Options Trading Positions

The COT report is a very strong and unique analytical tool and can be used by traders in many markets. The COT report will show trends as well as the conviction that traders have toward a trend. The COT report covers the most active traded futures contracts; currencies, interest rates and stock indexes.
Each week when the COT data is released, you can analyze the report by graphing or charting the data. The data is released at 3:30 pm each Friday, however, the report is made current on the Tuesday prior to the Friday release. The data is readily available from the CFTC’s website and is featured right on the home page of the website. It should be noted that COT data released by the CFTC is not easy to disseminate and is joined though a lengthy text file when it is released.
As discussed, there are three groups which make up the COT report. Those groups are commercial, large speculators, and small speculators. Although it is important to keep a close eye on the commercial speculators, the column the trader should keep the closest eye on is the large speculator. The commercial traders are typically hedging and are positioned toward the opposite direction of the non-commercial/large speculators.
In addition, the changes in long and or short positions can alert a trader about the specific trend investor sentiment. If a trader sees that long positions have diminished since the previous week and short positions have increased this would indicate that there is decline in bullish sentiment.
Market sentiment in general is very important to keep an eye on within the futures markets. When viewing market sentiment within the futures markets you should focus on the commercial trader/hedger as well as the non-commercial/large speculators. The small speculators are somewhat irrelevant when it comes to market sentiment.
Understanding market sentiment can help guide the trader in forecasting potential price moves. Although those who hedge are mostly concerned with mitigating risk they also want to place their hedge on when they believe that the product they produce is likely to experience a price decline.
There is evidence which indicates that the trader/hedger as well as the non-commercial/large speculators has superior forecasting capabilities which factors into the knowledge of which direction the market might be headed. When reviewing the overall sentiment of the futures market it is important to gauge this by trader size.
Farmers are one of the largest groups that rely on the futures markets to reduce their risk. Farmers are in business to grow crops and there is no certainty that the price of the crop that they are growing will increase in value. So, if a farmer is growing soybeans, for example and there is risk that the price of soybeans will decrease the farmer will hedge his/her risk by selling soybean futures contract on the CME Group Exchange. Each soybean futures contract consists of five thousand bushels of soybeans.
There is always the possibility that the price of soybeans moves higher by harvest time. If this happens there is a significant chance that the farmer would make a tremendous profit on his crop. However, the opposite could take place and soybean process move lower which would cause the farmer to take substantial losses. Again, for many farmers and agricultural commercials, hedging is about reducing risk while attempting to profit as much as possible on the crop yield.
Contrarian Market Indicator
Traders should have a solid understanding of what a contrarian market indicator is and how it can affect trading. Contrarian market indicators attempt to gauge the overall bullish and or bearish sentiment priced into a futures market.
Market indicators can lead or confirm overall price action. In addition, indicators can track the investing behavior associated to smart money.
The weekly data produced though the COT report is very useful but the data is not easily disseminated. It is much easier viewing the COT data through a chart which will depict the historical trading data. There are numerous free software applications from which you can upload the COT data. Also, the trader can plot their own COT charts but it is much more time consuming. When utilizing the COT report you can utilize it the same way you would use a customary technical indicator that analyzes only price and time. Filters can be applied to the report so that the trader has a better understanding on whether traders are becoming more or less bearish or bullish. With this knowledge the trader has the ability to trigger a trade exit or entry.
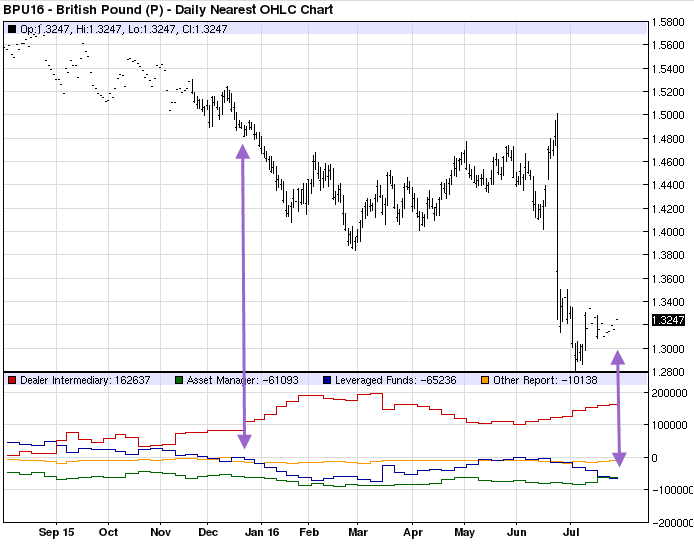
As noted earlier, there is a term frequently used amongst professional traders and that is “following the smart money”. What does following the smart money mean and who is the smart money? When doing your homework and researching the historical COT reports, you will clearly see at specific times (particularly during extreme COT instances) where the major players have positioned themselves. Researching the COT report will help the trader enter on the correct side of the market, and increase their chance for success.
For example, in the chart of the British Pound, you can see when leverage funds started to enter short position in January (blue line) which foreshadowed the decline of the price of the futures contract. In July of 2016, leverage funds were at the shortest they had been for more than 1-year. This could be a time where leverage funds are off sides and might be a time where the British Pound futures contract is ripe for a correction.
Hedging in the Futures Market
The commercial hedger is an entity that usually produces a commodity or an entity that will need to purchase a commodity within the future. These groups are looking to limit or reduce their risk by taking advantage of and hedging in the commodities markets.
Farmers are one of the largest groups that rely on the futures markets to reduce their risk. Farmers are in business to grow crops and there is no certainty that the price of the crop that they are growing will increase in value. Treasurers at large corporation will hedge their currency or interest rate risk using futures.
So, if a farmer is growing soybeans, for example and there is risk that the price of soybeans will decrease the farmer will hedge his/her risk by selling soybean futures contract on the CME Group Exchange. This group will generally have little incentive to alter their positions, which means that even if they are caught in the wrong direction, they will not need to exit their futures contracts. If a producer or farmer sells a futures contract and the price of the underlying rises, their losses from hedging will be offset by gains in the underlying commodity they own.
When hedging, there are two parts to the hedge. The first part of the hedge is a position in a commodity which is being created or has to be purchased. The second part of the position within the futures markets is what the hedger is limiting to reduce risk. Usually, one of the positions will shift in favor of the hedger and the other position will move against the hedger. In a perfect world, the hedge spread would not change during the time frame of the hedge.
There are instances where an organization or industry fails to hedge. A great example of an organization or industry failing to hedge would be when airlines fell asleep at the wheel and the price of oil jumped from $30 a barrel to close to $150 a barrel. Numerous airlines sustained massive loses and some went bust because of the high costs of fuel. If the companies that make up the airlines industry at the time properly hedged, a big portion of their losses would have been avoided.
Conclusion
In closing, the COT is a valuable tool which commodities traders can utilize to get an upper hand on the markets. You can use of the COT report to get a better understanding of what commercial hedgers, large trader and small speculators are doing within the commodities markets. The report can help commodities traders, forex traders (who are looking to increase their COT analysis in currencies), indices traders and fixed income traders.
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission or CFTC is the body which produces the COT report and has several responsibilities as they are associated to the futures markets. Some of the most important roles which the CFTC plays is making sure that the commodities markets are operating efficiently and that players within the futures markets are not manipulating the markets and committing fraudulent activity.
One of the most important elements of the COT report is its ability to help commodities traders see trends within the market. When actively monitoring the COT report through charts, commodities traders will have an active view of trends which are forming within the commodities markets. COT report analysis will benefit the individual trader and give him/her a better understanding on the direction of the particular market.
In addition, market sentiment will help the commodities trader to make better decisions associated to the direction of the markets. The groups which commodities traders should focus on are typically the managed money or non-commercial/large speculators. This will help the trader to be able to track the smart money and get a better sense of when to enter or exit the market.