 Arbitrage in the world of finance refers to a trading strategy that takes advantage of irregularities in a financial market. Forex arbitrage involves identifying and taking advantage of price discrepancies that can arise in the valuation of one or more currency pairs.
Arbitrage in the world of finance refers to a trading strategy that takes advantage of irregularities in a financial market. Forex arbitrage involves identifying and taking advantage of price discrepancies that can arise in the valuation of one or more currency pairs.
The general characteristic of real arbitrage is a “risk free” profit, but achieving this result usually involves taking a certain degree of risk during the execution of the trade. Often, the risk of execution actually exceeds the small profit that arbitrageurs commonly take in. A special type of arbitrage that does involve taking risk is known as statistical arbitrage where spreads between currency pairs are assessed and opposing positions taken when they get substantially out of line with historical norms.
While arbitrage trading is responsible for making large financial institutions and banks billions in profits, it has also been known to cause some of the largest financial collapses. This tends to occur when underlying parameters change and so the “risk free” profit in an arbitrage becomes instead a locked in loss. While arbitrage may appear like easy money for a forex trader, nothing could be further from the truth.
What is Arbitrage Trading in General?
Arbitrage can be defined as the simultaneous purchase and sale of two equivalent assets for a risk-free profit. In addition to the forex market, this trading strategy is actively employed in most financial markets, including the stock, commodity and options markets.
Basically, arbitrage takes advantage of discrepancies or irregularities in any given financial market, and involves situations where traders identify market conditions that allow them to take a small, risk-free profit when traded correctly. Forex arbitrage, as with arbitrage strategies in other markets, relies on these irregularities, which arise occasionally when markets trade inefficiently.
Arbitrage trade calculations, which were once done largely by hand or hand-held calculators, are now done in a number of way including forex arbitrage calculators, purpose made software programs, and even some trading platforms.
Because of the proliferation of such programs, financial markets have become even more efficient, which has further reduced the arbitrage opportunities in the forex market.
Several different methods can be used to arbitrage the forex market. For example, one such arbitrage technique involves buying and selling spot currency against the corresponding futures contract. Another form of currency arbitrage is called triangular arbitrage, which takes advantage of exchange rate discrepancies using three related currency pairs.
Other more complicated forms of forex arbitrage involve combining currency options, futures and spot; however, this type of arbitrage requires a significant initial margin deposit to execute since the selling of options is required. To add to the complexity of this type of arbitrage, a competent understanding of all three of those markets is imperative in the identification and execution of the arbitrage when it sets up.
 Using a Forex Arbitrage System
Using a Forex Arbitrage System
Before the advent of computers, arbitrageurs operating at banks and other financial institutions would work out their numbers with a hand held calculator and a pencil. Nowadays, to accurately identify and act on irregularities in the forex market, a suitable software program that identifies and automatically executes trades is typically used instead.
For retail currency traders, this type of forex arbitrage program generally comes in the form of an Expert Advisor or EA that works within an advanced forex trading platform such as MetaTrader 4 or 5. The EA constantly watches the forex market, and when an opportunity for an FX arbitrage arises, the program automatically executes the trade. This greatly improves a trader’s chances of locking in an arbitrage profit and/or being able to take advantage of a fleeting opportunity.
Nevertheless, many traders feel uncomfortable with automatically executed trades and prefer to make their own trading decisions. Such traders generally use trade alert or signal software. This type of software, much like the expert advisor software, constantly scans the market, but instead of automatically executing the trades, it will alert the trader when an arbitrage situation arises. The trader can then decide whether or not to act.
Some traders that use their own arbitrage software programs may also subscribe to remote signal alert services. Used in conjunction with their own programs, these services alert the trader’s software when an arbitrage situation arises in the market. The trader’s software then either alerts the trader of the arbitrage or automatically executes the trades.
Currency Futures Arbitrage Basics
Because of interest rate differentials, currency futures tend to sell at a premium or at a discount, depending on how wide the interest rate differential is between the currencies of the two countries involved.
If the currency futures contract is for the Pound Sterling quoted against the U.S. Dollar, for example, and the pertinent interest rate in the UK is at two percent, while U.S. rates are at only one percent, then Sterling would trade at a forward discount relative to the spot rate.
This is due to the carrying cost differential of one percent since you would be better off buying Sterling spot and holding it until the value date than buying it forward against the Dollar.
The above figures will now be used to illustrate how a six-month futures contract for Sterling can be arbitraged against the spot market. First of all, the following market and contract parameters will be used:
- The GBP/USD spot rate is trading at 1.2500.
- The 6-month futures contract for GBP/USD is trading at 1.2400.
- The 6-month interest rate on GBP is two percent.
- The 6-month interest rate on USD is one percent.
- The contract size is 1,000 units of currency.
The futures contract can be converted at the option of the seller of the contract into physical currency at the specified exchange rate when the futures contract matures in six months. The buyer of the 6-month GBP/USD futures contract would receive £1,000 and deliver $1,240 at the contract’s maturity in six months’ time.
The arbitrageur could then sell Sterling forward against the U.S. Dollar against the long futures contract. Alternatively, they could deposit £990.00 for six months at two percent. On the U.S. Dollar side, the trader would borrow $1,237 or the amount £990.00 would buy at the spot rate of 1.2500. A synthetic future would then be created converting £1,000 into $1,237 in six months’ time with a current cost of $1,237.
These numbers would indicate to an arbitrageur that the futures contract is trading slightly higher than it should be by three dollars per thousand. The arbitrage can then be established with the arbitrageur selling the futures contract for 1.2400 and buying spot with a net profit of $3.00 per thousand at the futures contract maturity. While $3.00 per thousand does not seem like a large profit on the trade, when the transaction is done in a large amount like $100,000,000, then the net profit would be a much more respectable $30,000.
Forex Triangular Arbitrage Explained
Many professional traders and market makers who specialize in cross currency pairs perform a process known as triangular arbitrage to lock in profits when the market driven cross rate temporarily deviates from the exchange rates observed for each component currency versus the U.S. Dollar. This popular currency arbitrage strategy takes advantage of the fact that the observed exchange rate for a cross currency pair is mathematically related to that of two other currency pairs.
Once the profit has been locked in by a triangular arbitrage, no further market risk exists. Nevertheless, the primary risk the cross currency trader still faces is counterparty risk, which would manifest into a significant problem if delivery on any leg of the three part transaction fails. Still, this risk is generally very low among well-established and creditworthy professional counterparties.
Traders performing a triangular arbitrage typically attempt to execute each leg of the three part transaction as simultaneously as possible. In addition to taking into account the costs of crossing any applicable bid off spreads to enter into the triangular arbitrage position, they also need to factor in their transaction costs to make sure they are locking in a profit.
Three currencies are involved in a triangular arbitrage, and traders use a mathematical formula to express the exchange rate for the cross currency pair as a function of the exchange rates for the two other related currency pairs that contain the U.S. Dollar as follows:
CCY2/CCY3 = USD/CCY3 x CCY2/USD
In the above equation, USD refers to the U.S. Dollar, while CCY2 is the base currency in the cross currency pair and CCY3 is the counter currency in the cross currency pair.
In addition, the term CCY2/CCY3 refers to the cross exchange rate of the counter currency CCY3 expressed in terms of the base currency or CCY2. The trader can also include any relevant transaction costs that may apply into computing an effective exchange rate.
The triangular arbitrageur performs the useful service of bring those markets back in line, and locks in a modest profit at the same time for their trouble. While retail forex traders rarely have this sort of opportunity, they can sometimes perform triangular arbitrages between the rates quoted by different online forex brokers.
Statistical Arbitrage in Forex Trading
In the forex market, statistical arbitrage involves seeking profit opportunities that arise from exchange rate discrepancies as determined by historical or predicted norms. Some traders prefer to call this spread trading rather than arbitrage because it does not technically result in locking in a risk-free profit as other true arbitrages do. Unlike other arbitrageurs operating in the forex market, statistical arbitrage traders therefore do actually take risk with their positions since the spreads between currency pairs that they seek to exploit can widen as well as narrow.
Most forex statistical arbitrage traders use mathematical modeling techniques and historical statistics consisting of the normal spreads between different currency pairs to determine which spreads are out of line and hence should see a narrowing over time. They will then endeavor to sell the overpriced currency pair and buy the underpriced currency pair.
If they do decide to engage in statistical arbitrage, a trader will also need to take some time to familiarize themselves with the mathematical and analytical methods used to identify such arbitrage opportunities. It may also be necessary for them to learn how to use and/or develop some computer systems to assist them in this process.
 Choosing a Suitable Currency Arbitrage Strategy
Choosing a Suitable Currency Arbitrage Strategy
Selecting the best FX currency arbitrage strategy to use for your particular situation and risk preference will probably depend on what markets you have access to, as well as whether or not you wish to take risk as an arbitrage trader.
For example, a professional cross currency trader and market maker will almost certainly be performing triangular arbitrage between their cross currency pair and the two other currency pairs that contain the same currencies quoted versus the U.S. Dollar. On the other hand, a trader with access to the currency futures market may instead wish to engage in futures arbitrage if they can deal in large enough amounts, have sufficiently small transaction costs and be able to identify arbitrage opportunities virtually in real time.
Finally, a retail forex trader with neither of those opportunities for arbitrage may be able to arbitrage quotes at different forex brokers to perform triangular arbitrage. Otherwise, they will probably be reduced to only having the ability to perform statistical arbitrage since they will most likely not have access to futures markets, Interbank pricing or clients dealing on their bid offer spreads. This also means their arbitrages will involve taking the risk of the spreads they perceive widening instead of narrowing based on their statistical analysis.
Another consideration when deciding whether to engage in arbitrage or what arbitrage strategy is right for you is that most arbitrages are done in as large a size as possible to maximize profits.
Accordingly, if you only have small transaction sizes to perform arbitrages with, then the proportionally modest potential income from this strategy may not interest you at all.
Forex Arbitrage Calculator Types
A concrete and popular example of a triangular arbitrate is often performed by professional EUR/JPY cross traders as part of their bread and butter business. When they see a large trade go through in any of the three related currency pairs of EUR/JPY, EUR/USD and USD/JPY, then the relationships between those markets gets sent briefly out of line as the big trade is assimilated into the exchange rates.
In particular, a EUR/JPY triangular arbitrage trader can readily enter the following transactions into an Excel spreadsheet to assist them in performing the following transactions in each currency pair to result in a locked in profit:
- Buy 1,000,000 EUR/USD at 1.1500
= Long 1,000,000 Euros and Short 1,150,000 U.S. Dollars
- Sell 1,000,000 EUR/JPY at 130.00
= Short 1,000,000 Euros and Long 130,000,000 Japanese Yen
- Buy 1,150,000 USD/JPY at 113.00
= Long 1,150,000 U.S. Dollars and Short 129,950,000 Yen
- Net Position or Profit
= Long 50,000 Yen at a rate of 113.00 for USD/JPY = US$442.48
When a retail trader is attempting to perform a triangular arbitrage between different online brokers, they can use an online arbitrage calculator like the one on the Forexop website that is shown in the screenshot image below. The same website also has an online calculator that helps you determine whether profitable futures versus spot arbitrage opportunities may exist.
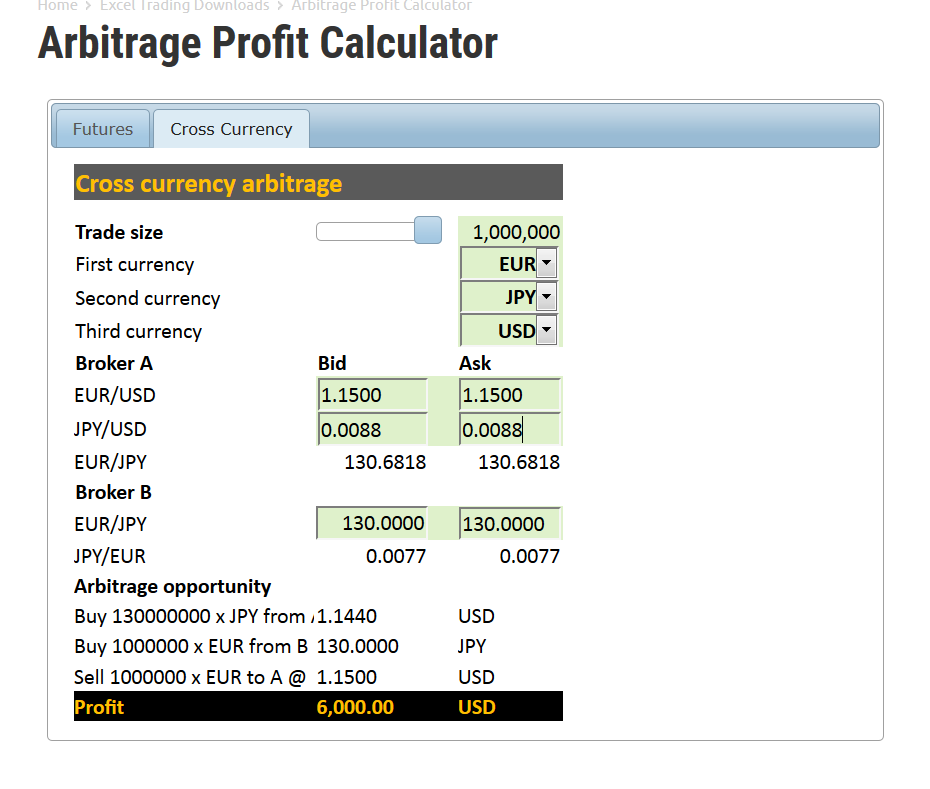
Using an Arbitrage Trading Program
An arbitrage trading program or ATP consists of computer software that can be used by a forex trader to enter orders simultaneously for spot, cross rate and currency futures contracts. This sort of software is usually employed by institutional or bank traders and involves executing large volume transactions in order to maximize arbitrage profits.
When involving futures arbitrage, the arbitrage trading program will enter either a long or a short position on an exchange traded futures contract, while the other order will involve taking the opposite position in the forex spot market or with an online forex broker.
Arbitrage trading programs are a form of program or algorithmic trading which involves the execution of trades in financial markets by automated computer programs. These programs follow a set of predetermined rules or algorithms when executing trades based one an identified opportunity to profit from an existing arbitrage between markets.