 Many novice forex traders who find they really enjoy speculating on currency pair movements start to wonder about how they might be able to make trading a career for themselves. Some of these traders may have initially gotten into forex trading to make a bit of extra cash for themselves.
Many novice forex traders who find they really enjoy speculating on currency pair movements start to wonder about how they might be able to make trading a career for themselves. Some of these traders may have initially gotten into forex trading to make a bit of extra cash for themselves.
As they become more familiar with the benefits that forex trading offers, they naturally begin to wonder whether focusing on trading full time is a viable option. The following article will discuss many aspects of trading forex for a living to help you make an informed decision for yourself.
Differences Between a Professional and Independent Trader
Depending on your educational background, professional contacts and demonstrable degree of proficiency in trading currencies, two basic types of currency trading jobs may be available to you if you want to start trading for a living.
The first type involves getting a job with a financial institution like a bank, a fund management firm or a multi-national corporation to trade currencies for their account. Unless you have some professional trading experience you can demonstrate, just about any initial forex trading job will be of an entry level nature where you start by acting as a clerk for a professional currency trader or market maker. This job typically involves writing down or electronically entering their trades for them. You can learn a great deal about trading just by watching a professional in action.
Alternatively, you could set up business as an independent forex trader trading currencies for a living. In contrast to becoming a professional forex trader, this can be done very quickly and without any particular background requirements.
Still, it will involve having or obtaining some trading capital and developing a trading plan you can follow as you operate in the currency markets. Being an independent trader is basically a self-employed position, and you will need to manage yourself and your trading related activities.
Some people do not like to take risks with their own money and like the idea of earning a salary as a professional forex trader instead of being a self-employed trader. They might prefer to be employed by a firm as a currency trader so that they can get paid to trade, and can place bets using the firm’s money instead. Most companies that employ forex traders offer good salaries and performance related bonuses.
While it may seem particularly attractive to find a job trading currencies for a bank, fund management firm or other financial institution, accepting any forex related employment position will still carry with it an expectation of performance by your employer. If you happen to lose money consistently when trading — or even if you fail to meet an employer’s established profitability targets — they may just fire you.
Types of Professional Forex Traders
Professional forex traders make a living trading currencies. In addition, most financial institutions have currency related trading positions for forex forward contracts and for those dealing in currency options and managing the risk of currency option portfolios.
In general, professional forex traders tend to fall into three main categories. These different roles require unique job skills, but each type requires that you are able to work well under stress. They are as follows:
- Market Maker – These professional traders usually work for a major financial institution like a bank. They generally make their money off the dealing spread they quote to clients on specific currency pairs that they specialize in. Market makers tend to be quick thinkers who seem especially good at performing mental arithmetic rapidly. They typically offset the positions they receive from clients quickly to minimize risk exposure. Market makers tend not to take longer term positions and instead mainly scalp the market in the currency pair they specialize in. They try to maximize gains as much as possible from trades and orders given to them by their institution’s clients.
- Strategic Trader – Such professional traders take calculated bets in the currency market on behalf of the company they work for. They tend to take longer term positions and are typically more adept at analysis, strategic planning and managing positions and money prudently. They might work at a fund management firm, a corporation or at a financial institution. They also work well under pressure.
- Customer Dealer – These professional traders deal directly with clients of the financial institution they work for but tend not to take risks. They keep in touch with market developments and can analyze market conditions. They can speak about them eloquently and give market advice. They are responsible for encouraging clients to deal and leave orders with their company. They tend to have sales oriented people skills and also work well under stress. They may take small forex positions, but they are largely responsible for adding value to client business.
The first two types of professional forex traders seem most suitable for those who enjoy taking risks for a living, while the third type seems best for people oriented individuals who prefer to give analytical advice on the forex market, rather than actually taking risks on it.
Getting a Job as a Professional Forex Trader
Interestingly, professional forex traders do not come from any particular type of educational background. Some currency traders never even finish college and just work their way up to being a trader within a financial institution or other organization.
Since there is no particular career path for a professional forex trader, becoming one takes determination, focus and probably also a good bit of luck. An exception might exist if you happen to know someone in the industry who is willing to vouch for you to the HR people within their company.
For starters, an aspiring professional currency trader should familiarize themselves with currency trading jargon and read extensively about what being a professional forex trader might involve. If they want to trade, they should also decide whether their personality type means they would probably do better as a market maker or as a strategic trader and market themselves appropriately to prospective employers.
Once you have done that basic research, you can start to circulate your resume to prospective employers who might be hiring currency traders. If you do not have a supportive educational background, like a degree in economics or finance for example, you might want to get a job with a smaller company first to get some hands on experience in a professional environment before applying to one of the major money center banks who often have large currency trading operations.
What Kind of Person wants to be an Independent Forex Trader?
The attraction of a potentially unlimited income, the freedom of working from home, and not having a boss to report to are probably some of the best and most common reasons why numerous people would like to become an independent forex trader.
While those working conditions may be ideal for some people, not all people have personality types that are consistent for success as an independent forex trader. Ideally, an independent forex trader should be a strategic thinker, an enthusiastic but sensible risk taker, and a good money manager. They will also need to be willing to invest a considerable amount of time and effort learning how to make a living trading forex, using techniques relevant to their unique personality.
Furthermore, any independent forex trader should be comfortable either taking risks with their own money or managing other people’s money. If you choose the latter, then you must be accountable and being willing to share profits with your investors. If you use only your own trading capital, you will reap all the rewards or losses, but when managing money, you will only get a percentage of the profits generated.
Don’t Give Up Your Day Job to Trade Independently Without Some Savings
Before going much further, it seems prudent to mention that — unless you happen to be independently wealthy and just trade currencies as a pastime — forex trading inevitably has its ups and downs in terms of profitability. This variability in income can get stressful for many people when they need the money they earn to pay for the necessities of life like food and shelter.
Accordingly, if you will need to make a living trading forex to support yourself and/or your family, it makes sense to make sure you have some savings put away in a separate account for security.
Before quitting your day job to jump into currency trading full time, you must make sure you are financially prepared to support yourself for at least 6 months to a year, without drawing any funds from your forex brokerage account.
Having some secure savings to draw upon set apart from your trading account funds will help you better weather any drawdowns in your trading account.
Setting Yourself Up as an Independent Forex Trader Requires a Plan
Although setting up shop as an independent forex trader doesn’t take much time, you must have a well- developed trading plan from the outset.
First of all, before you begin trading in the foreign exchange market, you should develop a basic knowledge and understanding of what market forces drive exchange rates. The exchange rate basically measures the level of supply and demand in a particular currency pair. Since the forex market can move in the blink of an eye and can even gap widely after major news and economic events, almost all online forex brokers caution potential currency traders that their losses can potentially exceed their deposit.
Furthermore, I suggest all new traders read the classic book: “Trading for a Living” by Alexander Elder and Richard Davidson. It will help the trader familiarize themselves with the optimal psychology, trading tactics and money management details that every trader should think about before taking the plunge into trading the financial markets.
In addition, every aspiring forex trader should seek to familiarize themselves with the two traditional forms of analysis that nearly all financial market traders tend to use.
Many traders use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis, since economic releases and geopolitical factors can affect the market considerably on a long term basis, while technical factors can dominate short term trading activity. Each of these forms of analysis is described further below:
- Technical Analysis – Traders using this popular form of analysis typically look at the movements that exchange rates have made and can compute various indicators based on observable price action. They might look for particular chart patterns, count waves and look for moving average crossovers or extreme market conditions, for example. After getting objective buy or sell signals from technical analysis, a trader may attempt to enter the market at specific chart points, perhaps by going long ahead of support or short ahead of resistance levels. Figure 1 shows an example of a historical exchange rate chart for the GBP/USD currency pair plotted using the MetaTrader 4 trading platform. Note the trend lines drawn to illustrate a chart pattern, the moving average indicators plotted over the exchange rate, and the Relative Strength Index oscillator drawn in the indicator box below.
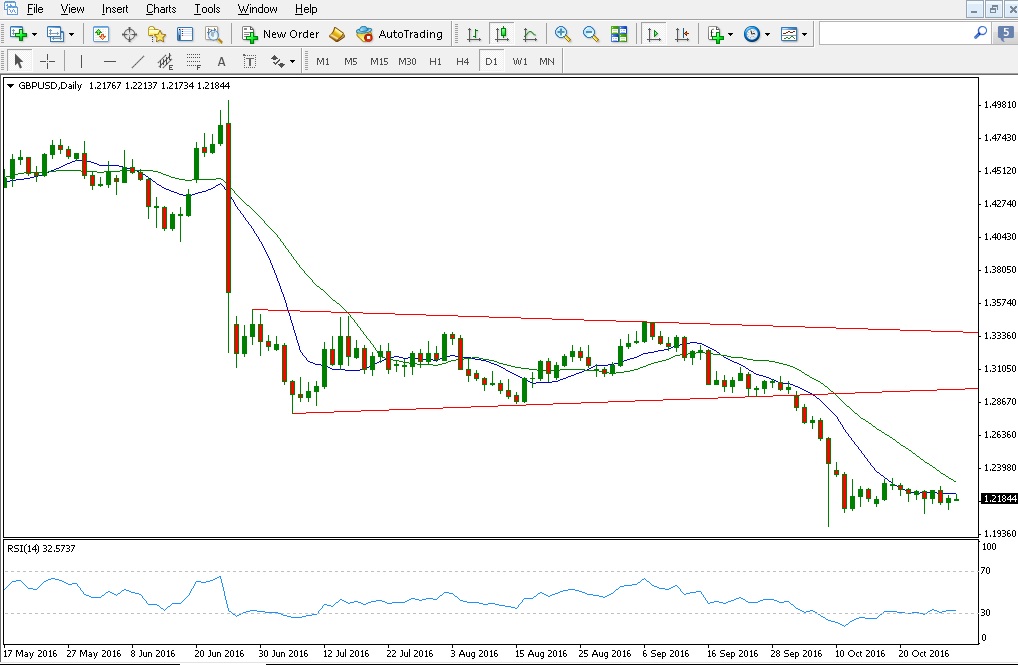
Figure 1: Historical exchange rate daily candlestick chart for the GBP/USD currency pair showing a breakout from a triangle chart pattern encased in red trendlines, the 10 day simple moving average drawn in blue and the 20 day in green, and the 14 day Relative Strength Index oscillator shown in the indicator box at the bottom in pale blue. This chart was produced with the popular MetaTrader 4 forex trading platform supported by many online brokers.
- Fundamental Analysis – Traders using this form of analysis might attempt to determine the relative value of currencies according to underlying economic conditions of a particular region. They often place a special emphasis on reviewing the economic calendar for key upcoming news releases. These items can include a country’s employment numbers, a central bank’s interest rate releases and monetary policy statements, Gross Domestic Product, the Consumer Price Index, and a slew of other data that fundamental traders continually keep track of.
After acquiring a basic understanding of underlying elements that influence currency valuations, the potential trader is ready to develop a suitable trading plan. A trading plan generally gives the conditions under which a trader will consider entering and exiting trades, along with a prudent money management strategy they intend to use and contingencies for adverse or changing market situations.
Forex Demo Accounts
Before opening a live funded account, the novice forex trader would be well advised to implement their trading plan in a demo account. This is an account offered by most online forex brokers that allows for trading without having to fund the account. The virtual account reflects semi real market conditions and is an excellent way for a person without forex market experience to get a firsthand look at how the currency market trades.
After successfully testing the trading plan in a forex demo account, an aspiring independent trader can feel far more confident about taking their trading plan into a live account. While the process may sound simple, a trading plan must be strictly adhered to in a disciplined manner if long term success is the goal.
By trading their plan successfully in the demo account first, the prospective forex trader will probably have:
(1) determined the possibilities and risks involved in currency trading,
(2) implemented a suitable money management strategy, and
(3) limited the possibility of losing their entire account during volatile markets.
In addition, the objectivity that having a trading plan provides should ideally take the trader’s emotional state out of the trading equation and help them make better trading decisions.
Selecting a Forex Broker
Once the independent trader feels confident in their plan and wishes to proceed, a live account must be opened with a trustworthy online forex broker.
Selecting a suitable broker to partner with will require a certain amount of research. It is also important for U.S citizens to keep in mind that as of this writing, most forex brokers, based outside the United States, will not service people domiciled in the United States.
Another important consideration is the broker’s regulating body. In the United States, forex brokers must register with the Commodities Futures Trading Commission or with the National Futures Association to do business with U.S. clients. In the UK, the Financial Services Authority is the regulating body and in the EU, a broker should be regulated under the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive or MiFID.
In addition to regulation, the prospective trader should investigate the broker’s reputation with its clients. Various websites exist for clients to post forex broker reviews. Also, the trader will need to choose among the several different types of forex broker models according to the type of trading they plan on engaging in.
They should therefore find out whether their potential broker is a market maker with a dealing desk or DD, or a No dealing desk or NDD broker, and whether they conduct business through an Electronic Communications Network (ECN) or if they use Straight through Processing (STP).
Once the potential trader has selected their broker and funded their account, they are ready to take the plunge and begin trading.