 An important consideration to take into account when comparing forex brokers is how they execute customer transactions and whether or not they take the other side of each order and transaction you deal through them.
An important consideration to take into account when comparing forex brokers is how they execute customer transactions and whether or not they take the other side of each order and transaction you deal through them.
In practice, just about all forex brokers will operate under one of the five common broker business models, although some brokers might use a hybrid of two or more of these models.
Since the differences between these models mean brokers might have substantially variable order execution methods, it pays to understand how each of these models works so that you can select the best order execution method to suit your forex trading business.
The following sections will describe and contrast these various forex broker models to assist you in making the important decision about what type of broker to select to partner with.
The Electronic Communication Network or ECN Forex Broker Model
Forex brokers that use an Electronic Communication Network or ECN model provide their customers with a means for obtaining direct access to the Interbank forex market for pricing and execution that usually consists of an ECN trading platform.
Traders should try out the trading platform offers by ECN brokers they are considering using to determine the best ECN broker platform for their particular needs.
In effect, by using an ECN execution model for client transactions, it means that a forex broker has No Dealing Desk or NDD standing as they operate as a liaison between their clients and the greater currency market. Choosing to deal though an NDD forex broker helps a trader cut out both the market maker and their dealing desk who may both wish to profit from their transactions.
Most ECN forex brokers will display order information and exchange rates in real time as they fluctuate, and their pricing on transactions comes directly from the Interbank forex market. Also, since trades are processed electronically, ECN forex brokers typically have a reduced human error rate.
One substantial advance of dealing with this sort of broker is that the risk of re-quotes should be virtually eliminated. This can really be a substantial benefit to news traders who typically like to benefit from the high level of market volatility surrounding the release of major economic data such as the NFP report or other news events.
Another notable advantage of using an ECN broker is that they allow traders to deal on spreads that are typically considerably tighter than that quoted by a single market maker. Nevertheless, because the dealing spreads for ECN trade execution are not set at a customary fixed width and can fluctuate substantially — especially at times when the market is exceptionally volatile — this can introduce some uncertainty into the pricing a trader can routinely access.
Some forex brokers using the ECN model will charge a flat deal execution fee on a per trade basis as a commission, which can be beneficial for those who tend to trade larger amounts less frequently.
Alternatively, some other ECN brokers simply widen the trading spread their client can deal on and so they charge fees that are proportional to the amount dealt on each trade. This latter type of ECN broker may better suit traders who prefer to trade frequently in smaller amounts.
The Straight Through Processing or STP Forex Broker Model
Forex brokers that use Straight Through Processing (STP) generally have a fully automated dealing system for their clients to use. They do not operate a dealing desk, and hence are considered a NDD or No Dealing Desk broker. This type of forex broker model is also sometimes referred to as the A-Book forex brokerage model.
Such a STP dealing system will typically process each trade electronically and enter them directly into a select group of Interbank forex market participants, known as liquidity providers, for execution at competitive prices.
Orders are entered anonymously on behalf of clients by the broker into this subset of the forex market, the members of which are chosen by the broker based on established dealing relationships.
The most notable advantage of using an STP broker is that no human related errors, delays or costs should be associated with each transaction. This means that a trader can avoid having other people intervene in their deals that might introduce unwanted errors, costs or delays.
Another benefit of using an STP forex broker is that liquidity tends to be greater since prices are obtained from a number of market participants instead of from only one liquidity provider like in the market maker model. This generally means better fills, more accurate quotes and tighter dealing spreads when compared to the service provided by a forex broker that only has a single source for its quotations.
The Direct Market Access or DMA Forex Broker Model
Forex brokers will sometimes use a Direct Market Access or DMA model to execute transactions for their clients. This automated service matches client orders with dealing prices offered by professional market makers at banks or other major liquidity providers. Furthermore, in the DMA model, all client orders get passed on directly to liquidity providers.
True Direct Market Access involves non-dealing desk execution only at the market price, which is a more transparent process from the trader’s perspective. In contrast, the instant execution services offered by some brokers usually involves the broker filling the order themselves and then deciding whether or not to offset the risk with other liquidity providers. This tends to be less transparent to the client.
DMA brokers typically offer only variable spreads to their clients, rather than a fixed dealing spread. In addition, the deal execution platform provided by DMA forex brokers tends to add either a fixed mark up to client transactions or charge a per trade commission.
In general, ECN forex brokers will also offer a DMA service to their clients. Although some STP forex brokers will offer a DMA service to their customers, that is not always the case.
Market Maker Forex Broker Model
A forex broker that acts as a market marker typically operates a dealing desk or DD and makes their money by quoting a bid/ask spread to clients. Such market makers operate with the intention of capturing as much of that spread as possible for its own benefit as profit.
This broker model implies that the broker will usually provide a two sided market price with fixed dealing spreads that depend on each currency pair quoted to its clients.
This type of forex broker model is also sometimes referred to as the B-Book forex brokerage model.
Although this model involves taking market risk, since the broker effectively trades against its clients, market making has traditionally been a popular model for forex brokers due to the high loss rate among retail traders and the fact that more of the dealing spread is typically captured as profit from client transactions using this model than in charging a simple commission.
The chart shown below in Figure 1 illustrates just how many retail forex traders over-optimistically think they can make money trading currencies versus the far smaller number of such traders who actually do make money.
These results indicate that 84 percent of retail traders believe they can make money trading forex versus the only 30 percent who actually made money when trading.
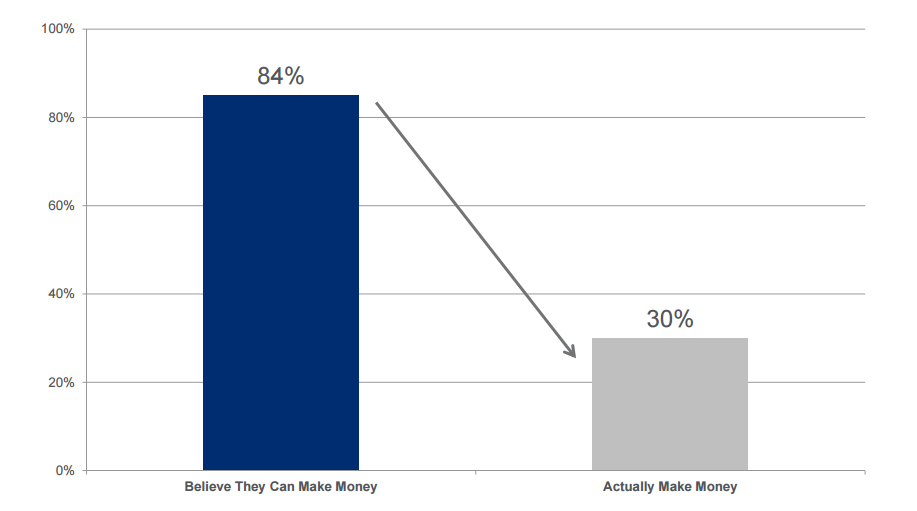
Figure 1: Comparison of the percentage of retail forex traders that believe they can make money versus those who actually do. This profitability data was based on individual broker filings with the NFA in the second quarter of 2013.
Market makers do sometimes feel the need to widen their dealing spreads in times of high market volatility. In addition, a market maker might elect to re-quote prices if the market has moved before the client chooses to deal. Quoted dealing prices are typically held for a very short period of time for a client, which is traditionally described as being: “as long as the breath is warm”.
It is important to note that a forex market maker can manipulate or shade their quoted price above or below the existing market exchange rate depending on their market view and their existing position in inventory. Some market makers also make it a practice to read their clients’ intentions and will lower their price if they think the client is a seller or raise their price if they think the client is a buyer.
An even more serious issue is known as “spread popping” where a market maker might adjust their spread to cause a stop loss order to be executed. Market makers operating at large financial institutions can even put enough pressure on the market so that a stop loss order is executed that they then benefit from by filling with the transactions that they made at better prices.
Also, when orders are placed with market makers by forex traders, the market makers can elect to delay order execution or trade ahead of and around the orders in an attempt to profit further from them.
Brokers using the market maker model always take the opposite side of a client transaction. This means that when the client is a seller, the market maker will need to buy from them, and when the client is a buyer, the market maker will need to sell to them. This sets up the possible risk of a conflict of interest occurring between the market making forex broker and their clients.
The pricing transparency level of market making brokers tends to be lower than with brokers using other deal execution methods. In addition, clients can be profiled by a market making broker as typically being either winners or losers, and this can help the market maker decide whether to hold or offset the client’s deal in the market after its execution.
Furthermore, if the client’s trade is a large one, the market maker will probably offset any undesirable risk with other major liquidity providers, such as large commercial banks operating actively in the Interbank forex market. They might call around to a series of market makers asking for prices and then select the best quote or quotes available to fill the amount they wish to offset.
Hybrid Forex Broker Models
Some forex brokers use a hybrid model for processing client transactions consisting of a combination of two or more types of forex broker models. This can give a trader the best of both worlds if they think a combination of models would work best for their trading strategy.
In addition, some forex brokers offer one type of execution for certain accounts, and another type for other accounts. An example of this might be where large volume traders can open up an ECN account, while mini lot traders have to go through a dealing desk since large liquidity providers generally have no interest in transacting small amounts like that.
An example of an especially common hybrid involves blending the ECN or DMA and STP models together to create a fully electronic forex dealing service. This popular mixture allows a forex broker to fully automate the order entry, dealing spread pricing, and trade execution aspects of their deal execution business.
Furthermore, using this sort of ECN or DMA and STP hybrid model typically allows a forex broker to reduce their costs substantially after system development has completed. This means they can either offer a discounted deal execution service, or they can focus their human staff’s efforts on providing high quality customer service, education, market analysis and sales instead to help distinguish their brand from the competition.
Another notable advantage of this hybrid model is the relatively low error rate since humans working for the forex broker do not involve themselves directly in the deal execution process.
Nevertheless, programming bugs, security breaches, hacking, power or data loss, and system failure errors can still arise even with a fully automated ECN or DMA and STP forex dealing system, and such problems can be harder to recover from since no human memory or voice recording of a transaction is available to refer to.
The Multilateral Trading Facility or MTF Forex Broker Model
An interesting evolution in the retail forex market involves the model used by some online forex brokers who operate in a manner similar to regulated financial exchanges, although they do not actually have that status. In the European Union, these brokers qualify as and are called Multilateral Trading Facilities under the MiFID regulations, while they might be known as Alternative Trading Systems in the United States.
Basically, an MTF is an investment company that puts buyers and sellers together to form contracts among themselves. Such participants do so depending on a set of rules via the system’s internal operating procedures.
Some online forex brokers operate as MTFs, and these can be an interesting solution for traders looking for more of an exchange traded environment to operate in at lower cost than commission hungry regulated exchanges like the Chicago International Monetary Market where currencies can also be traded.
In general, an MTF offers a trader decent transparency, a fair trading system, good execution of transactions, and reduced brokerage costs relative to the traditional regulated exchanges.
Choosing the Right Type of Forex Broker Model for Your Needs
Selecting the most advantageous type of online forex broker to best fit your trading needs will typically depend on what type of trading strategy you prefer to use. In addition, the amount of trading capital that you have available to use in your trading account and your typical trading frequency can be important considerations.
Many traders also prefer to avoid using market makers due to the potential conflict of interest involved and the non-transparent pricing they offer that can result in an execution on a trade at a price away from the prevailing market.
Furthermore, those trading in larger amounts would tend to gravitate toward executing their transactions via an ECN or STP forex broker due to the fact that their trades will be entered directly into the highly liquid Interbank forex market, thereby probably reducing their dealing spreads, execution times and human error risk.
Choosing a model that involves electronic order entry will also alleviate the trader from having to deal with a market maker and their dealing desk. It also tends to reduce the risk and inconvenience of experiencing re-quotes on their orders in fast market conditions where the exchange rate is moving quickly.
In contrast, those traders that like to participate in social trading activities might have different preferences. For example, they might like to see statistics about how the crowd is positioning as a whole so that they can follow along or fade the majority. This might require a specialized form of forex broker model that displays such useful social trading information. This social trading feature tends to be supported by Multilateral Trading Facilities or MTFs, and positioning information can also be obtained from regulated exchanges.